Enterprise resource planning (ERP) Systems refer to a type of software that organizations use to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk management, and compliance, and supply chain operations.

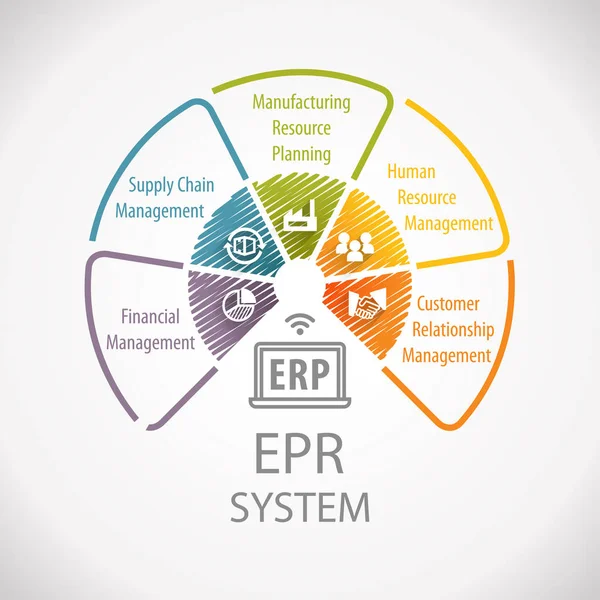
ERP stands for “Enterprise Resource Planning” and refers to software and systems used to plan and manage all the core supply chain, manufacturing, services, financial and other processes of an organization. Enterprise Resource Planning software can be used to automate and simplify individual activities across a business or organization, such as accounting and procurement, project management, customer relationship management, risk management, compliance, and supply chain operations.
Individual ERP applications can offer software as a service (SaaS). In contrast, a complete suite of ERP applications forms an ERP system that can effectively communicate and bring together business processes to enable a flow of data between the applications, typically through common databases either on-site/on-premise or in the cloud.
ERPs connect every aspect of an enterprise. An ERP software system allows for better performance and project management that helps plan, budget, predict and accurately report on an organization’s financial health and processes.
Working of ERP system
The primary purpose of an ERP system is to increase the organizational efficiency of an organization by managing and improving how company resources are utilized. Enhancing and reducing the resources necessary without sacrificing quality and performance are keys to effectively enhancing business growth and profitability.ERP systems typically cover all aspects of business operations and commonly provide:
- An integrated system
- Common database
- Real-time operation
- Support for all applications/components
- Standard user interfaces across applications/components.
- On-premise, cloud-hosted, or SaaS deployment.
ERP software can collect and compare metrics across departments and provide several different reports based on roles or specific user preferences. The data collected makes finding and reporting faster and gives a complete view of business performance with exclusive insights on how resources are being spent.

ERP synchronizes reporting and automation by reducing the need to maintain separate databases and spreadsheets that must be manually merged to generate reports. This combined data collection and reporting offers valuable insight, such as cutting costs and streamlining processes, providing the information to make real-time business decisions.
Types of ERP Systems: Cloud vs. On-Premise vs. Hybrid
There are three main types of ERP systems that function with different deployment model options. The most common types of ERP systems include cloud ERP, on-premise ERP, and hybrid ERP.
- On-Premise ERP software is implemented onsite and maintained in physical office space within an organization, hosted on the company’s computers and servers for complete control, support, and ownership of the entire system once implemented.
- Cloud-based ERP software is a web-based solution known as Software as a Service (SaaS). An organization accesses and stores data on any device with an internet connection, usually through a subscription. The software provider supports continual support, updates, training, and flexible customizations.
- “Hybrid” ERP software refers to a combined implementation of cloud-based and on-premise ERP system solutions. The combination of hosting and deployment services vary by provider. These models can allow ERP users to migrate between delivery models or integrate benefits not available in the existing implementation.
Different ERP vendors support other deployment model options. Combinations of options often referred to as “hybrid” deployment, may offer various hosting and deployment services. These hybrid models can provide users with a flexible ERP solution and integrate benefits that may not have been available within the existing implementation.
How to Select ERP Systems
Picking and deploying an ERP system can be a daunting task with many software solutions to choose from. When selecting an ERP system, the software must meet the needs and goals of your company while having the support required to implement an ERP system.
Here is a quick checklist to review when first comparing ERP Systems to help narrow down your options.
Checklist for Selecting ERP Systems
Does the ERP software/vendor that is being considered:
- Meet your system requirements?
- Meet/align with company goals?
- Integrate/compatible with currently existing systems?
- Have partner Network/Availability for local support?
- Offer training/support options?
- Have references and recommendations from customers?
- Continuously improve and develop to utilize new technology and adapt to challenges?
Once the ERP options have been narrowed down to solutions that are most compatible with your current systems and goals, it can be helpful to review the benefits and features of the systems with key decision-makers of the organization—having the insight and support of these decision-makers can boost the adoption and support of an ERP implementation throughout the organization.
ERP Systems can Enhance Your Fashion, Retail, Apparel, Or Footwear Business in Other Ways
- Make your business more agile: In a rapidly evolving business climate, responding to change is essential. A sound ERP system is flexible, modular, and scalable enough to adapt to shifting market dynamics and evolving customer needs. You can initially implement specific applications that make sense now and add seamlessly integrated applications as needed as your business grows.
- Drastically increase efficiency and productivity: Inefficient spreadsheets, manual workflows, and outdated software can inhibit your business growth. An ERP system can streamline your entire organization and put your data all in one place, enabling more accurate reporting and a more efficient, collaboration-based, and data-driven work environment.
- Save on unnecessary costs: Running your business with an ERP system creates efficiencies that make your business leaner as it grows. Many companies report that they can expand without adding additional staff or IT costs. The cost of implementing an ERP system is easily eclipsed by the ROI of a more efficient, fully optimized business environment.
- Improve security and accessibility: You can reduce your risk and hardware costs by moving your ERP to the cloud. Embrace the future of information systems with a modern ERP hosted in a secure cloud. Moving your ERP applications to the cloud allows you to scale, extend and upgrade quickly. It also increases visibility and accessibility even further, taking full advantage of an ERP system’s capabilities.
- Gain a professional partner: When you upgrade to an ERP system, you also gain the partnership of your ERP implementation provider and all the support – from implementation and training to software support to community membership – that they have to offer. Some ERP systems have dedicated user groups and communities that open up entire networks of industry innovators and dynamic brands.
- Grow your business: An ERP system can eliminate inefficiencies, wasted time, and wasted resources, empowering your business to thrive and flourish. If you’ve been burdened by an inability to keep up with demand because you’re limited by conventional systems or stagnant legacy ERP systems, upgrading to a modern ERP system frees your business to realize its true growth potential.
Its a Wrap!
There are as many reasons for successful ERP implementations as there are for failed projects. However, success seems to be often measured by whether or not the project came in on time and under budget. Whereas fully utilizing the system to achieve improved business practices appears to be ignored.